
10 Enigmatic Facts About Roy Wood Jr - Facts.net - Source facts.net
Editor's Notes: The comprehensive guide to "Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies" published today, exploring the significance of understanding this virus and tackling the risks it poses.
Through extensive analysis and expert insights, our team has compiled this guide to empower individuals with the knowledge and resources necessary to effectively address this enigmatic virus.
Key Takeaways:
| Key Difference | Description |
|---|---|
| Transmission | Through saliva of infected animals, primarily through bites |
| Impact | Fatal neurological disease, primarily affecting the central nervous system |
| Prevention | Vaccination, post-exposure prophylaxis, and animal control |
Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies covers vital aspects of this virus:
Understanding Rabies and Its Impact:
Lyssavirus's Unique Characteristics:
Prevention and Control Measures:
FAQ
Lyssavirus: Understanding The Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies Behind Rabies is a comprehensive online resource that explores the enigmatic lyssavirus, the causative agent of rabies. Here are some frequently asked questions to address common concerns and clarify misconceptions about this intriguing virus.

15 Enigmatic Facts About The Gaius Octavian Augustus Statue - Facts.net - Source facts.net
Question 1: What are the different types of lyssaviruses?
There are several recognised species of lyssaviruses, including:
- Rabies virus (RABV)
- European bat lyssavirus type 1 (EBLV-1)
- European bat lyssavirus type 2 (EBLV-2)
- Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV)
Question 2: How is rabies transmitted?
Rabies is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, typically dogs or bats. The virus is present in the saliva of infected animals and can enter the body through wounds or mucous membranes.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of rabies?
Rabies has two main clinical forms: furious rabies and paralytic rabies. Furious rabies is characterized by hyperactivity, aggression, and hydrophobia (fear of water). Paralytic rabies, on the other hand, causes progressive muscle weakness and paralysis.
Question 4: Is rabies curable?
Once symptoms of rabies manifest, the disease is usually fatal. However, timely post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), which involves vaccination and administration of rabies immune globulin, can effectively prevent the onset of the disease.
Question 5: How can I protect myself from rabies?
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent rabies. Avoiding contact with wild animals, especially bats, is also crucial. If bitten or scratched by an animal, promptly seek medical attention and inform the authorities.
Question 6: What is the global burden of rabies?
Rabies is a significant global health concern, with an estimated 59,000 human deaths annually, primarily in Asia and Africa. The World Health Organization (WHO) aims to eliminate dog-mediated rabies by 2030 through mass vaccination campaigns and public health measures.
Understanding the lyssavirus and rabies is crucial for preventing and controlling this deadly disease. By raising awareness and promoting responsible animal ownership, we can contribute to the global efforts to eliminate rabies.
To learn more about lyssaviruses and rabies, refer to the comprehensive resource: Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies
Tips
Understanding Lyssavirus, the virus behind rabies, is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. The following tips provide valuable insights into the virus and its implications:
Tip 1: Recognize the Diversity of Lyssaviruses
Lyssavirus encompasses multiple species, each associated with different host animals. Understanding this diversity helps mitigate the risk of transmission and enables targeted prevention strategies.
Tip 2: Identify Early Symptoms
Early detection is crucial for rabies treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on the infection site and virus species, but common signs include fever, headache, and paresthesia (prickling or numbness).
Tip 3: Practice Precautionary Measures
Rabies is primarily transmitted through contact with infected animal saliva. Vaccination, avoiding contact with wildlife, and proper wound management reduce the risk of infection.
Tip 4: Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If bitten or scratched by an animal that may be infected, seek immediate medical attention. The sooner treatment is initiated, the higher the chances of survival.
Tip 5: Enhance Surveillance and Research
Continuous surveillance and research are vital for understanding Lyssavirus evolution and developing effective control measures. Monitoring animal populations, genetic studies, and vaccine development contribute to rabies prevention and eradication.
Tip 6: Promote Public Awareness
Educating the public about Lyssavirus, its symptoms, and prevention measures is crucial for containing the disease. Outreach programs, school curricula, and community campaigns raise awareness and promote responsible behavior.
Tip 7: Support Vaccination Efforts
Vaccination plays a significant role in rabies control. Support vaccination campaigns, particularly in high-risk areas, to create protective barriers against the virus.
Tip 8: Collaborate for Effective Control
Rabies prevention requires collaboration among healthcare professionals, veterinarians, and public health authorities. Sharing data, coordinating surveillance efforts, and implementing joint strategies strengthen control measures.
By following these tips, individuals and communities can contribute to the understanding, prevention, and control of Lyssavirus and rabies.
Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies
Lyssavirus, the enigmatic genus of viruses that causes rabies, is a significant threat to human and animal health. Its diverse aspects warrant thorough understanding to combat its impact. Here are six key dimensions of Lyssavirus:
- Neurotropic: Targets the nervous system
- Deadly: Fatal if untreated
- Transmissible: Spreads through contact with saliva
- Ancient: Originated long before human evolution
- Diverse: Multiple genetic variants
- Preventable: Controlled by vaccines
19 Enigmatic Facts About Glow Stick Tic-Tac-Toe - Facts.net - Source facts.net
Understanding these key aspects is crucial for developing preventive strategies, effective treatments, and surveillance systems. Rabies remains a global health concern, and tackling it requires comprehensive knowledge of Lyssavirus. Through continued research and international collaboration, we can mitigate its impact and protect both human and animal populations.
Lyssavirus: Understanding The Enigmatic Virus Behind Rabies
Lyssaviruses are agents of a fatal zoonotic disease named rabies, which can affect all mammals, including humans. The virus causes a progressive, fatal encephalomyelitis characterized by a range of clinical manifestations, including furious and paralytic forms.
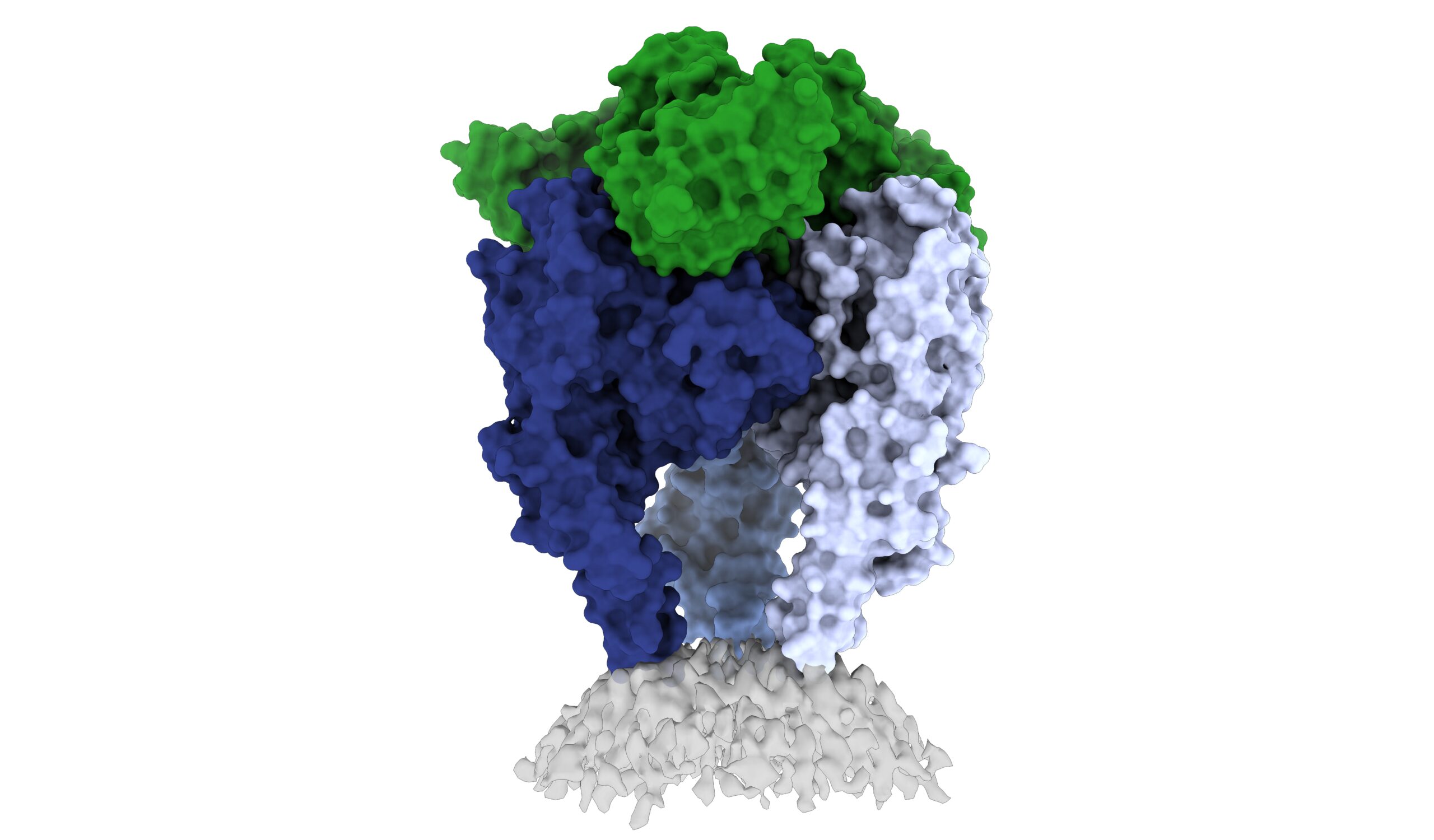
» Rethinking the rabies vaccine - Source www.lji.org
Understanding the Lyssavirus is crucial for rabies prevention and control. The virus is mainly transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, typically via bites or scratches. It has a complex life cycle, involving replication in the host's central nervous system and dissemination throughout the body.
Effective rabies management relies on comprehending the virus's epidemiology, pathogenesis, and immune response. Public health interventions focus on pre-exposure prophylaxis for individuals at risk and post-exposure prophylaxis in case of potential exposure. Advances in diagnostic techniques, such as molecular assays, have significantly improved rabies diagnosis and surveillance.
Table: Key Insights on Lyssavirus and Rabies
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Causative Agent | Lyssavirus, a neurotropic virus belonging to the family Rhabdoviridae |
| Transmission | Primarily through the saliva of infected animals, via bites or scratches |
| Clinical Manifestations | Furious and paralytic forms, with progressive encephalomyelitis |
| Diagnosis | Molecular assays and other laboratory tests |
| Prevention and Control | Pre-exposure prophylaxis, post-exposure prophylaxis, animal vaccination |
Conclusion
Lyssavirus remains a significant public health concern globally. Ongoing research and surveillance efforts are crucial to improve our understanding of the virus, its variants, and the epidemiology of rabies. By continually advancing our knowledge, we can effectively prevent and control this deadly disease, ensuring the health of both humans and animals.
Rabies control measures must prioritize public education, animal vaccination, and accessible healthcare, particularly in endemic regions. With a comprehensive approach, we can work towards eliminating human rabies and its devastating consequences.